Keratoconus
What is Keratoconus ?
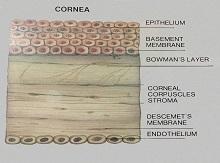
Keratoconus is the leading cause of blindness especially among the youth in East Africa. A normal cornea (see definition of cornea below) is shaped like a watch glass, but sometimes it starts thinning and bulging; this is known as Keratoconus (Kerato meaning Cornea and Conus like a cone). In such cases, the cornea cannot perform its main function of focusing light rays entering the eye on to the retina due to its distorted shape.Here the middle part of the cornea becomes weak and thin. As a result, it cannot withstand the pressure of the eye causing the cornea to bulge.
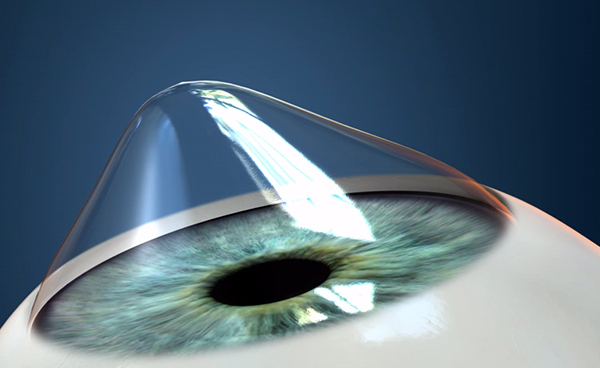
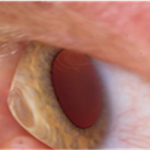
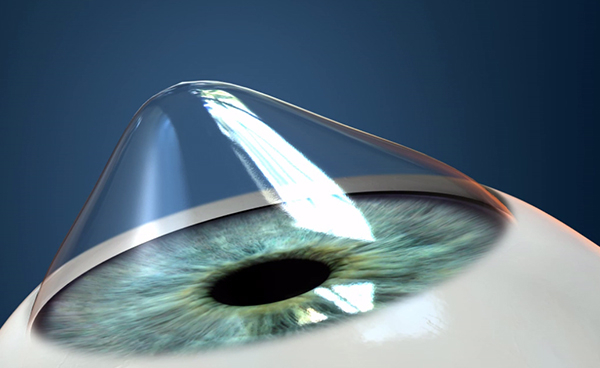
Normal Cornea
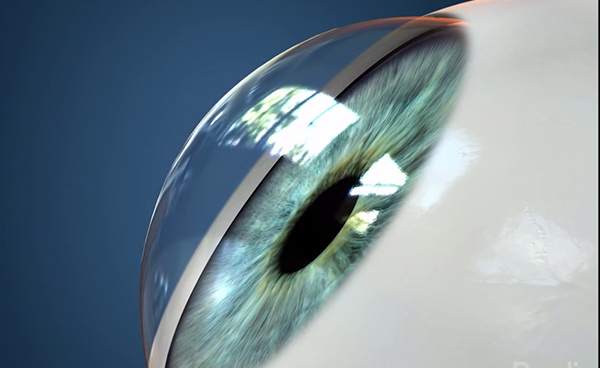
Eye With Keratoconus (The cornea looks like a cone)
The exact cause of Keratoconus is not known, but it is believed that it could be due to a malfunction in the enzymes, which make the stroma (please see cross-section of the cornea) weak. It could also be associated with allergy and there is some evidence that it may be hereditary.
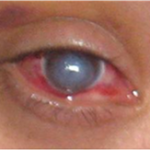
Keratoconus is also linked with over exposure to sunlight, improper contact lens fitting and constant eye rubbing. If there is progressive stretching in the Descemet’s membrane, it leads to rupturing of the membrane and can cause hydrops, where the cornea becomes completely cloudy as shown in the picture below
Diagnosis
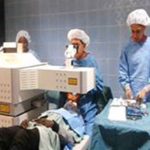
Diagnosis of Keratoconus is done through Topography and Tomography, which is a gold standard for Keratoconus but your optician, will suspect Keratoconus if there is frequent change in the astigmatism of the eye and despite of giving the correct glasses the vision of the quality is not very good and there is difference in glasses prescription between your two eyes.
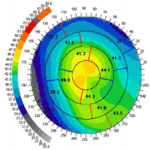
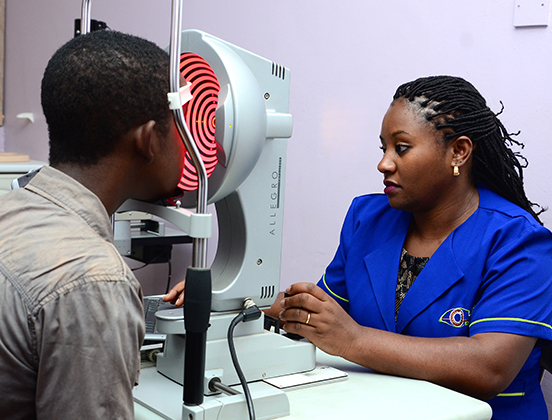
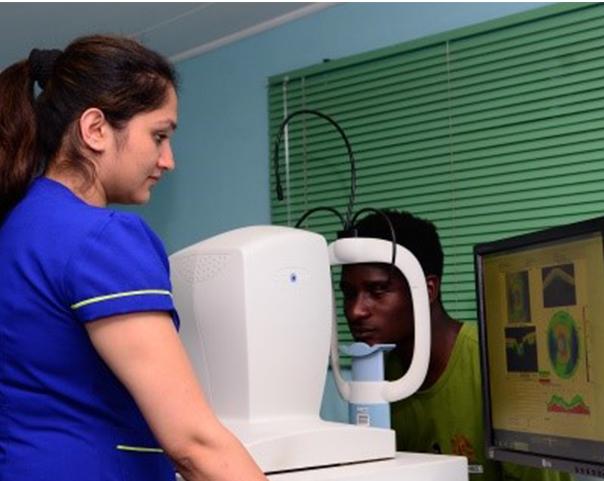
Topography Test
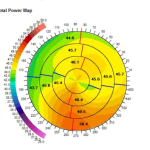
During topographic examination, concentric rings are projected on the cornea and images are taken by a specialized camera. This image is then colour coded to represent the corneal surface. Cool colors like green and blue are flatter meridians like grass and lake, while hot colors like red.

Topography Test
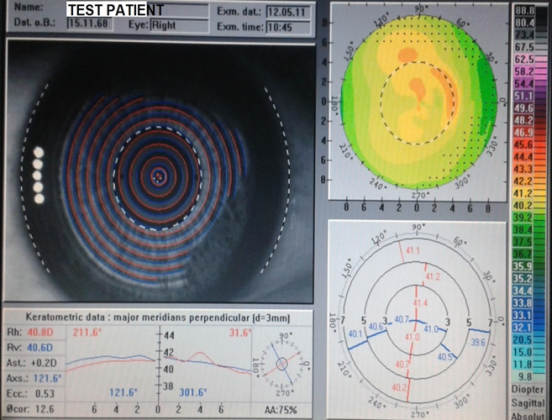
Topography showing Normal cornea
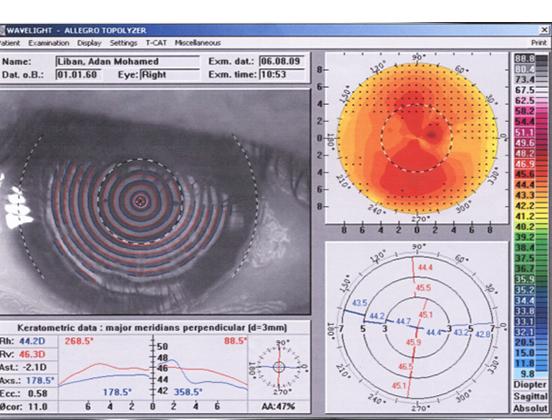
Topography showing Keratoconus
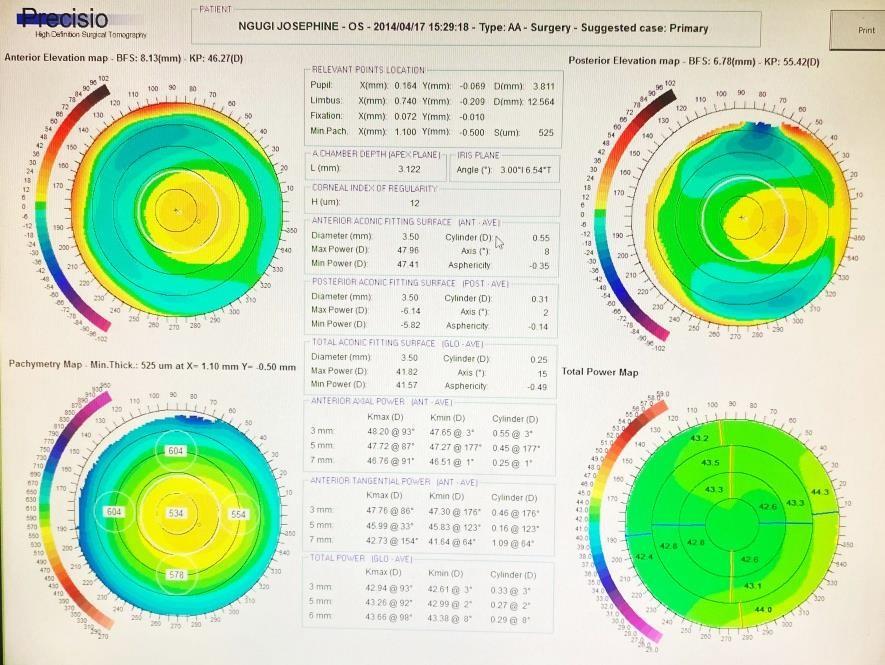
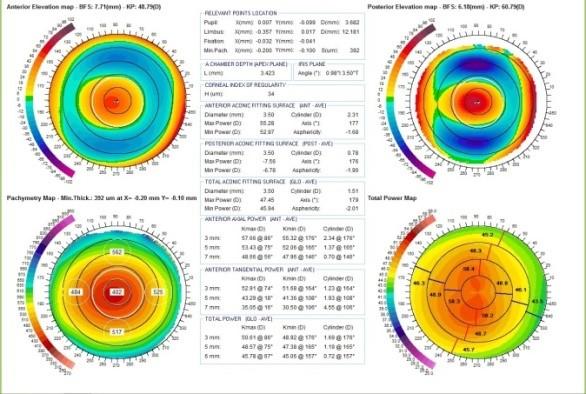
Tomography with the cutting edge Precisio machine
The Precisio machine is then used to assess the back surface of the cornea as well as checking the surface as well. The Precisio machine examines 39,000 points in the eye and gives an accurate measurement on the corneal thickness (Pachymetry).

The Tomography Machine
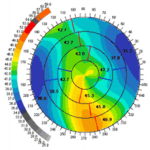
Normal Precisio
Precisio With Keratoconus
Tomography with the cutting edge Precisio machine
Precisio is a device where the front and back part of the cornea is scanned by 39,000 spots and the entire cornea is color coded where fright readings are shown by blue or green, steep millidiance are shown by red. Tomography is the ideal gold standard of diagnosing Keratoconus.
The second important diagnosing tool is OCT epithelial map. Usually, the top most layer of the cornea is about 52 microns, and when keratoconus is present, there is bulging of the cornea which bulges in tops cells of the epithelium. When epithelial becomes thinner, it is an early sign of developing keratoconus.
Diagnosis of Keratoconus by Epithelial Mapping
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) test: This test detects early signs of Keratoconus.
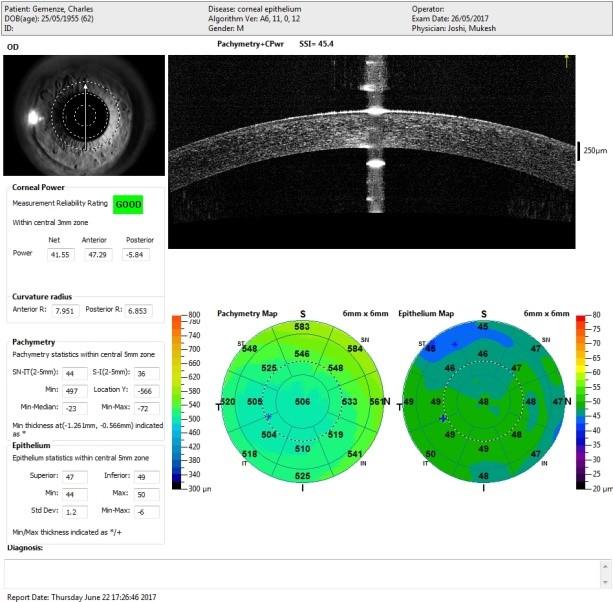
Normal Tomography Test of Epithelial.
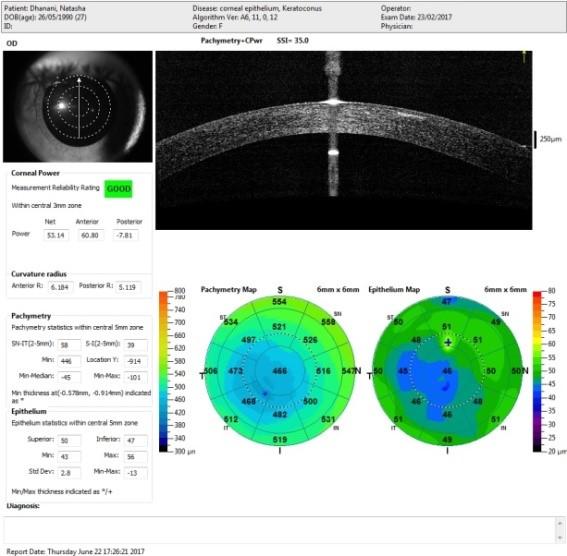
Tomography showing early signs of Keratoconus.
Treatment
At Laser Eye Centre we have the following protocol for treating Keratoconus
- Early to moderate stages we do central corneal regularization followed by Cross-Linking.
- Fairly advanced stage only Cross-Linking
- Very advanced stage Corneal Transplant.
Central Corneal Regulation (CCR) Followed By Cross-Linking
First Stage Central. Corneal Regulation
This is done by reshaping the cornea; we reduce the size of the cone by very specialized laser which takes only 34 seconds.
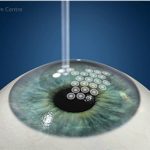
Second Stage: Collagen Cross-Linking
This is the latest treatment for Keratoconus and was invented by Prof Seiler (Switzerland), and Prof Spoerl (Germany). Cross-Linking has become the standard treatment to treat Keratoconus
Central Corneal Regulation (CCR)
Keratoconus gives rise to irregular irregular Astigmatism and patient’s vision is not improving with glasses and because of atopic conjunctiva contact lenses is a challenge.
The principle of Corneal Regularization is to reshape the cornea and make the Keratoconus cone as flat as possible and convert the irregular irregular Astigmatism into regular Astigmatism.
In CCR, the surgeon treats the Keratoconus cone by shifting the cone in the Centre.
With 1000 Hz frequency, IVIS laser will reshape the top of the cone and the surrounding area.
This is achieved by performing laser on the side of the cornea which is thicker. Therefore, not damaging the cornea that is already thin.
What Is Cross-Linking?
- This is a mini-invasive treatment, which has been proven to strengthen the weak corneal tissues.
- Riboflavin eye drops (vitamin B12) are applied to the patient’s eye for half an hour.
- The Riboflavin is then activated by Ultra Violet light. An interaction between the ultra violet light and the Riboflavin soaked cornea leads to the strengthening and stiffening of the collagen fibers in the cornea.
- This does not allow Keratoconus to progress further. In our clinical practice, cross linking is helpful for 90% of Keratoconus patients but it does not work if the Keratoconus is very advanced.
- The standard length of treatment is 10 minutes.
IF KERATOCONUS IS DIAGNOSED AT AN EARLY STAGE, CROSS-LINKING IS THE TREATMENT OF CHOICE AS IT IS NON–INVASIVE AND RELATIVELY SIMPLE.
New breakthrough Cross linking treatment:
At Laser Eye Center, it is now possible to reduce the cross-linking procedure time to 5 minutes.
We can do this by incorporating our C-Ten (1000Htz) laser and the CCL-365 platform.
The overall result is better vision than cross-linking alone in a fraction of the time using cutting edge and safe technology.
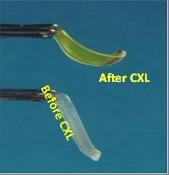
Corneal Strip Before and After Cross linking.
After cross linking the cornea has become stiff.
Cross-Linking In Progress
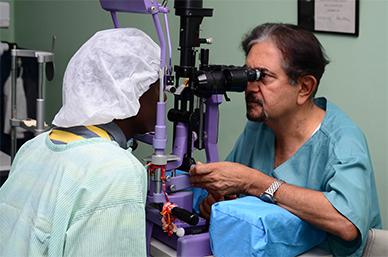
Examining Patient before starting Cross-Linking
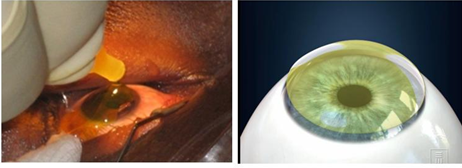
Instilling Riboflavin eye drops to the patient’s eyes
Riboflavin Shielding
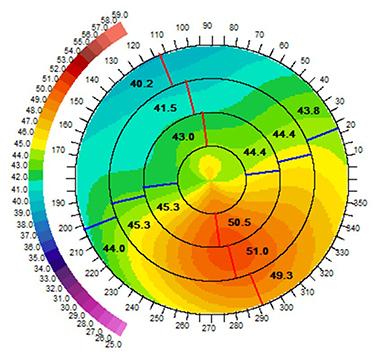
Before CCR and CXL
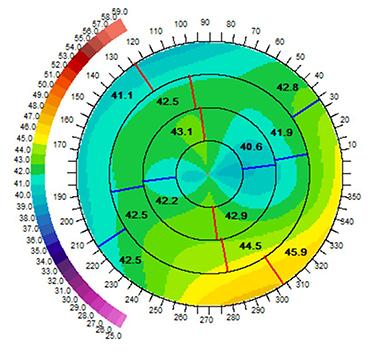
After CCR and CXL
Laser Eye Centre is the first centre in Asia and Africa to offer cross linking treatment in any form and is also the first and only centre to offer the 10 minute Cross-Linking / CCL-365 platform.
- Dr. Joshi was appointed as a global expert on Keratoconus during the 5th International meeting European Society of Cataract and Refractive Surgeons (Germany 2010).
- Dr.Joshi has also been invited by various international societies to share his experience on cross-linking; we at Laser Eye centre were the first to start cross-linking in Africa and Asia.
- An ophthalmologist must undergo training for cross-linking certification so that he/she can do this treatment.
Corneal transplant/ Keratoplasty
Corneal Transplant (also known as Keratoplasty) is usually carried out if the patient’s Keratoconus is at a very advanced stage where contact lenses or cross-linking are not possible.
The best solution to such cases would be corneal transplant or Keratoplasty (please see the Keratoplasty section of the website).
FAQS
How many years of experience does Dr. Joshi have in keratoplasty?
What are the factors of success or failure of corneal transplant?
What is the main cause of the vision deteriorating if the corneal transplant was done many years ago?
Laser eye centre is the first Centre in Kenya that puts toric implants in the eye after Keratoplasty.